Introduction
What's Silverback?
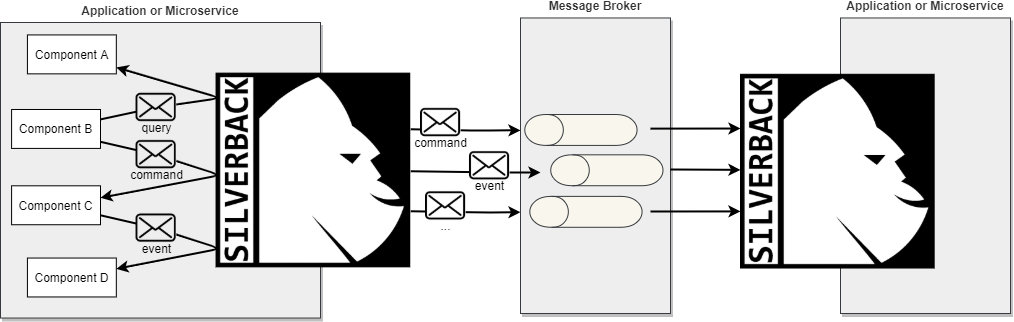
Silverback is essentially a bus that can be either used internally to an application or connected to a message broker to integrate different applications or microservices.
Samples and examples
This documentation is filled with examples and code snippets, plus an entire section is dedicated to fully functional ready-to-run code samples. The plan is to improve the samples section over time, adding real-world scenarios that demonstrates how to take advantage of the various Silverback features in your projects.
A few notes about the code:
- Even though it will compile and work just fine (most of the time), it is intended for demo purpose only and don't automatically imply the best practices are being in place nor it is by any mean production ready. Sometimes some shortcuts may have been taken to keep the code compact, readable and focused on the aspect that is being highlighted.
- Not all examples are ported to each message broker implementation, but most of them can be adapted to work with either Kafka, MQTT or Rabbit with minimal effort (unless some broker-specific features are being used, of course).
Packages
Silverback is modular and delivered in multiple packages, available through nuget.org.
Core
Silverback.Core
It implements a very simple, yet very effective, publish/subscribe in-memory bus that can be used to decouple the software parts and easily implement a Domain Driven Design approach.
Silverback.Core.Model
It contains some interfaces that will help organize the messages and write cleaner code, adding some semantic. It also includes a sample implementation of a base class for your domain entities.
Silverback.Core.EntityFrameworkCore
It contains the storage implementation to integrate Silverback with Entity Framework Core. It is needed to use a DbContext as storage for (temporary) data and to fire the domain events as part of the SaveChanges transaction.
Silverback.Core.Rx
Adds the possibility to create an Rx Observable over the internal bus.
Integration
Silverback.Integration
Contains the message broker and connectors abstraction. Inbound and outbound connectors can be attached to a message broker to either export some events/commands/messages to other microservices or react to the messages fired by other microservices in the same way as internal messages are handled.
Silverback.Integration.Testing
Includes some utilities to help writing automated tests involving Silverback.Integration.
Silverback.Integration.Kafka
An implementation of Silverback.Integration for the popular Apache Kafka message broker.
Silverback.Integration.Kafka.SchemaRegistry
Adds the support for Apache Avro and the schema registry on top of Silverback.Integration.Kafka.
Silverback.Integration.Kafka.Testing
Includes a mock for the Kafka message broker to be used for in-memory testing.
Silverback.Integration.MQTT
An implementation of Silverback.Integration for MQTT.
Silverback.Integration.MQTT.Testing
Includes a mock for the MQTT message broker to be used for in-memory testing.
Silverback.Integration.RabbitMQ
An implementation of Silverback.Integration for the popular RabbitMQ message broker.
Silverback.Integration.RabbitMQ.Testing (coming soon)
Includes a mock for the RabbitMQ message broker to be used for in-memory testing.
Silverback.Integration.HealthChecks
Contains the extensions for Microsoft.Extensions.Diagnostics.HealthChecks to monitor the connection to the message broker.
Silverback.Integration.Newtonsoft
Contains the legacy implementations of IMessageSerializer, based on Newtonsoft.Json.
Event Sourcing
Silverback.EventSourcing
Contains an implementation of an event store that perfectly integrates within the Silverback ecosystem.
Glossary
The following list serves as introduction to the terminology and types used in Silverback.
Publisher
An object that can be used to publish messages to the internal in-memory bus. It is represented by the IPublisher or (better) the more specific IEventPublisher and ICommandPublisher interfaces, that can be resolved via dependency injection.
Subscriber
A method (or delegate) that is subscribed to the bus and will process some (or all) of the messages that will be published or consumed from a message broker (since those messages are automatically pushed to the internal bus).
Broker
A message broker, like Apache Kafka or RabbitMQ. It is represented by the IBroker interface and is used internally by Silverback to bind the internal bus with a message broker. It can be resolved and used directly but that shouldn't be necessary for most of the use cases.
Producer
An object used to publish messages to the broker. It is represented by the IProducer interface.
Consumer
An object used to receive messages from the broker. It is represented by the IConsumer interface.
Endpoint
Identifies a specific topic or queue. It also contains all the settings to bind to that endpoint and is therefore specific to the message broker implementation. It is represented by an implementation of the IEndpoint interface.
Inbound Endpoint / Consumer Endpoint
An endpoint that is consumed and whose messages are relayed into the internal bus, where they can be consumed by one or more subscribers. It is represented by an implementation of the IConsumerEndpoint interface such as the KafkaConsumerEndpoint.
Outbound Endpoint / Producer Endpoint
Silverback can be configured to automatically publish some messages to the message broker, observing the internal bus and relaying the messages matching with the configure type. The outbound/producer endpoint specifies the topic or queue where those message have to be produced. It is represented by an implementation of the IProducerEndpoint interface such as the KafkaProducerEndpoint.
Behavior
Multiple behaviors are chained to build a sort of pipeline to process the messages transiting across the internal bus, the consumer or the producer. They are used to implement cross-cutting concerns, isolate responsibilities and allow for greater flexibility. Some built-in behaviors are responsible for serialization, error policies enforcement, batching, chunking, encryption, etc.